When designing a modern application, chances are that you will need a database to store data. There are many ways to architect software solutions that use a database, depending on how your application will use this data. In this article, we will cover the different types of database architecture and describe in greater detail a three-tier application architecture, which is extensively used in modern web applications.
What is database architecture?
Database architecture describes how a database management system (DBMS) will be integrated with your application. When designing a database architecture, you must make decisions that will change how your applications are created.
First, decide on the type of database you would like to use. The database could be centralized or decentralized. Centralized databases are typically used for regular web applications and will be the focus of this article. Decentralized databases, such as blockchain databases, might require a different architecture.
Once you've decided the type of database you want to use, you can determine the type of architecture you want to use. Typically, these are categorized into single-tier or multi-tier applications.
What are the types of database architecture?
When we talk about database architectures, we refer to the number of tiers an application has.
1-tier architecture
In 1-tier architecture, the database and any application interfacing with the database are kept on a single server or device. Because there are no network delays involved, this is generally a fast way to access data.
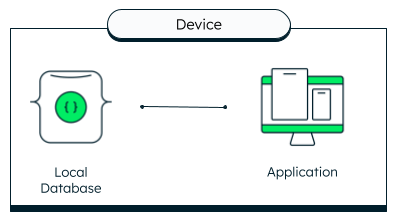
On a single-tier application, the application and database reside on the same device.
An example of a 1-tier architecture would be a mobile application that uses Realm, the open-source mobile database by MongoDB, as a local database. In that case, both the application and the database are running on the user's mobile device.
2-tier architecture
2-tier architectures consist of multiple clients connecting directly to the database. This architecture is also known as client-server architecture.
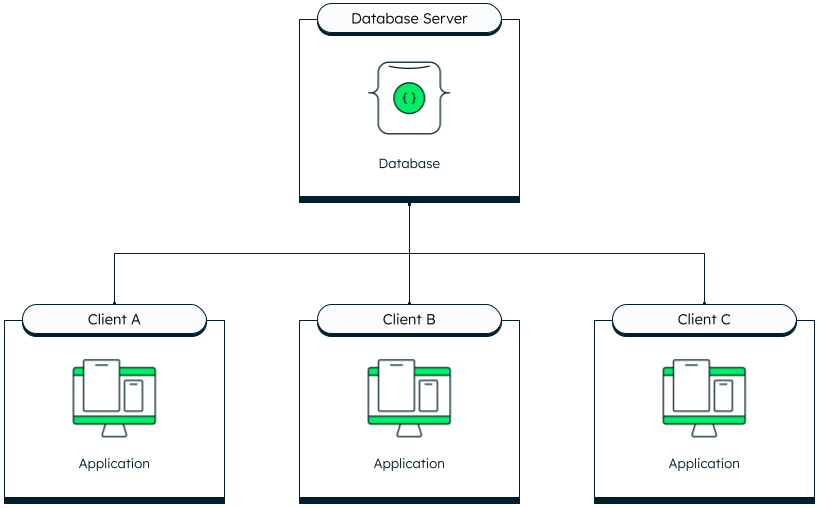
In a 2-tier architecture, clients are connecting directly to a database.
This architecture used to be more common when a desktop application would connect to a single database hosted on an on-premise database server---for example, an in-house customer relationship management (CRM) that connects to an Access database.
3-tier architecture
Most modern web applications use a 3-tier architecture. In this architecture, the clients connect to a back end, which in turn connects to the database. Using this approach has many benefits:
- Security: Keeping the database connection open to a single back end reduces the risks of being hacked.
- Scalability: Because each layer operates independently, it is easier to scale parts of the application.
- Faster deployment: Having multiple tiers makes it easier to have a separation of concerns and to follow cloud-native best practices, including better continuous delivery processes.
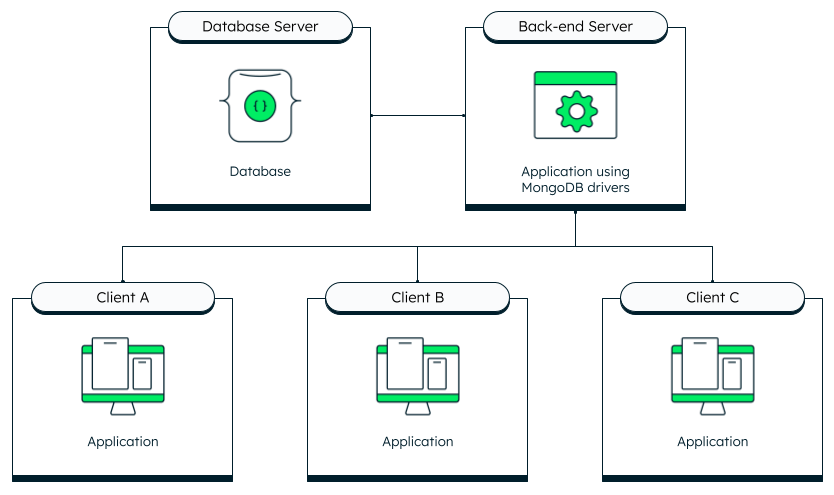
In a 3-tier architecture, the information between the database and the clients is relayed by a back-end server.
An example of this type of architecture would be a React application that connects to a Node.js back end. The Node.js back end processes the requests and fetches the necessary information from a database such as MongoDB Atlas, using the native driver. This architecture is described in greater detail in the next section.
What are the three levels of database architecture in MongoDB Atlas?
The most common DBMS architecture used in modern application development is the 3-tier model. Since it's so popular, let's look at what this architecture looks like with MongoDB Atlas.
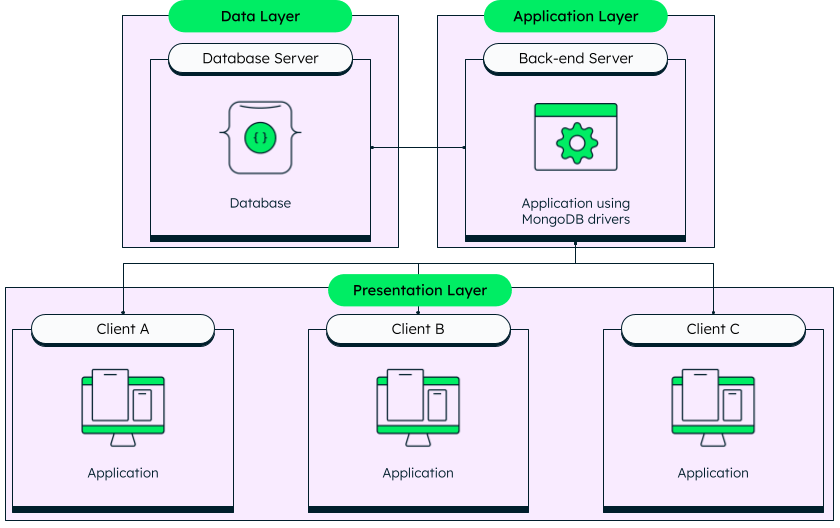
A three tier application is composed of three layers, the data, the application, and the presentation.
As you can see in this diagram, the 3-tier architecture comprises the data, application, and presentation levels.
Data (database) layer
As the name suggests, the data layer is where the data resides. In the scenario above, the data is stored in a MongoDB Atlas database hosted on any public cloud---or across multiple clouds, if needed. The only responsibility of this layer is to keep the data accessible for the application layer and run the queries efficiently.
Application (middle) layer
The application tier is in charge of communicating with the database. To ensure secure access to the data, requests are initiated from this tier. In a modern web application, this would be your API. A back-end application built with Node.js (or any other programming language with a native driver) makes requests to the database and relays the information back to the clients.
Presentation (user) layer
The final layer is the presentation layer. This is usually the UI of the application with which the users will interact. In the case of a MERN or MEAN stack application, this would be the JavaScript front end built with React or Angular.
Summary
In this article, you've learned about the different types of database architecture. A 3-tier architecture is your go-to solution for most modern web applications. However, there are other topologies that you might want to explore. For example, the type of database you use could be a dedicated or a serverless instance, depending on your predicted usage model. You could also supplement your database with data lakes or even online archiving to make the best use of your hardware resources. If you are ready to concretize your database architecture, why not try MongoDB Atlas, the database-as-a-service solution from MongoDB? Using the realm-web SDK, you can even host all three tiers of your web application on MongoDB Atlas.